What is 3D Scanning?
CLASSIFICATION
1. No Contact Scanning:
Millions of
points on the xyz coordinate system can be easily captured via non-contact
scanning. This data provides a fuller, more accurate picture of an object's
size and shape than a physical part measurement could. The likelihood of human
error is decreased because this approach can detect the entire portion,
including warpage. Active and passive scanners are additional categories for
non-contact scanning.
2. Passive Scanning:
Because they
do not produce radiation itself, passive scanners are frequently affordable.
They rely on sensing ambient radiation that has been reflected. A digital
camera is frequently a good option for this.
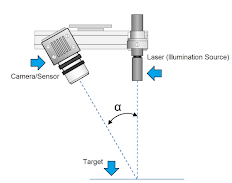
3. Laser Triangulation:
In this
method, a point or line is projected onto an object using a laser, and a sensor
placed at a certain distance from the laser's source then records the
reflection. The 3D measurements of the part can be determined by interpreting
the reflection angle.
4. Contact 3D Scanning:
By rubbing different locations on an object's surface with the ball of a probe, you can digitise it. Instead of using organic free-form shapes, individual 3D data points are acquired to accurately define an object's geometric form. With a coordinated measure machine, digitising is performed (CMM). One of three scanner methods is possible for CMMs:
a system of rigid arms attached to a carriage in a perpendicular position, an articulated arm with angular sensors and rigid arms and for mapping massive objects with internal chambers or overlapping surfaces, a combination of the two can be used
PROCESS
3D Laser Scanning Method An object to be laser scanned is placed on the digitizer's bed. Specialized software drives the laser probe above the surface of the object. The laser probe projects a line of laser light onto the surface, while two sensor cameras continuously record the changing distance and shape of the laser line as it sweeps along the object in three dimensions (XYZ).
Data obtained as a result
The shape of the object appears on the computer monitor as millions of points called a "point cloud" as the laser moves around capturing the entire surface shape of the object. The process is extremely fast, collecting up to 750,000 points per second, and extremely precise (to.0005′′).
APPLICATIONS
1. Education
All throughout the world, 3D scanning is beginning to be used more often
in classrooms. Students with very limited 3D CAD modelling abilities can build
and 3D print fully unique models that would be next to impossible to produce
with software alone by using sculpting clay or a comparable media. We recently
began work on a lesson plan that has students design, scan, and print their
very own ergonomic pen. We are major proponents of 3D scanning in the
classroom. We will be developing a lot of lesson ideas in the future that
utilise both 3D scanning and 3D printing.
2. Art/History
Artists and
art historians are increasingly utilising 3D scanning. One of the main
applications in this sector is the scanning of artefacts to produce
reproducible 3D printed replicas or for preserving and curating. Any type of
cultural asset can be categorised, measured, analysed, and even shared among
the study community thanks to 3D scanning. With 3D scanning, artists may include real-world photos and
objects into their creations. A designer of home goods recently spoke with us
about his desire to scan organic things like leaves and feathers and
incorporate them into his creations, such as on a decorative vase or bowl.
3. Medicine/Health
Nowadays, 3D technology has established itself as a vital instrument in the health sector. Among all industries, prosthetics is one of my personal favourite uses for 3D technology. With the use of 3D scanning, prosthetic limbs can be designed and manufactured with a level of accuracy that ensures optimal comfort, movement, and pain relief. This technology takes a tiny fraction of the time and money of more conventional techniques when combined with 3D printing. More and more, 3D scanning is being utilised by medical practitioners to thoroughly examine bodily components, such as before surgery.
4. Engineering
Engineering
is another industry with a lot of promise for 3D scanning. Rapid prototyping
and reverse engineering are made incredibly simple by the ability to scan any
thing and then modify it using CAD. It is easier to investigate mechanical
qualities and undertake precise measurements.








Comments
Post a Comment